Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. What is rate-based rule?
- 3. What you can specify in the rate-based rule
- 4. Setting rate-based rules
- 5. Limitations when using WafCharm
- 6. Conclusion
1. Introduction
In this post, we will take a look at the rate-based rules.
When you use rate-based rules, you can block numerous requests from the same IP address.
We hope you can utilize this explanatory post for creating a rate-based rule on AWS WAF.
2. What is rate-based rule?
Rate-based rules are explained by AWS as below:
A rate-based rule tracks the rate of requests for each originating IP address, and triggers the rule action on IPs with rates that go over a limit. You set the limit as the number of requests per 5-minute time span. You can use this type of rule to put a temporary block on requests from an IP address that's sending excessive requests.
In other words, it is a rule that blocks a requester that sends multiple requests by determining them using a threshold.
This rule only works for a single requester, so it cannot act as an explicit DDoS attack countermeasure, but you could think of it as a way to mitigate the attack.
You can also expect this rule to prevent attackers to try multiple passwords on the log-in page (i.e., dictionary attack) or catch attackers who are accessing the website to add load (i.e., brute force attack).
3. What you can specify in the rate-based rule
Let’s check the details of the actual rules you can create.
In rate-based rules, you can create a single rule or combine conditions.
For example, if you want to catch continuous access to a certain path, you can create a rate-based rule to URI that has “/login”.
You can also use conditions like certain countries or IP addresses, or even combine them. If you want to, you can apply a rate-based rule for access to “/login” from countries outside of Japan.
The minimum threshold is 100 requests/5 minutes.
When the request exceeds the threshold, the requester’s IP address will be blocked. When the number of requests falls below the threshold, the restriction will automatically be removed.
4. Setting rate-based rules
In this post, we will create a rule to block requests to a certain path when it comes from countries other than Japan with a threshold of 100 requests/5 minutes.
If this is your first time creating a rule, also refer to the blog posts below.
- Part 1: [New AWS WAF] Summary of Changes
- Part 2: [New AWS WAF] AWS Management Console Operation (Managed Rules)
- Part 3: [New AWS WAF] AWS Management Console Operations (Original Rules)
- Part 4: [New AWS WAF] AWS Management Console Operations (Pattern Sets & Rule Groups)
- Part 5: [New AWS WAF] JSON Explanation
The procedures are as below.
- Create a rule
- Edit using JSON editor
Create a rule
Select “Rate-based rule” under the Type section.
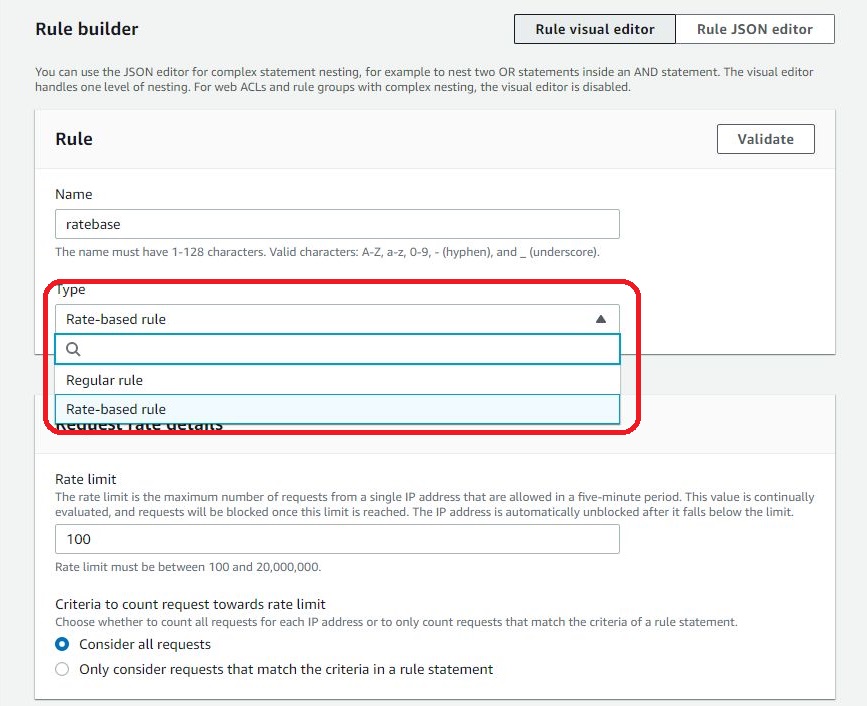
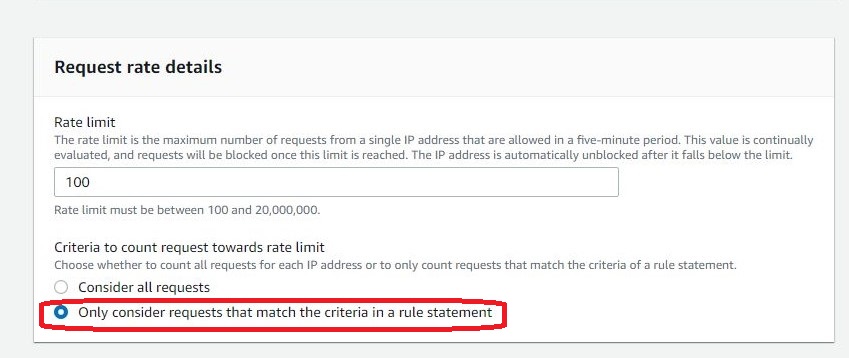
Enter “100” for the “Rate limit” input and choose the “Only consider requests that match the criteria in a rule statement” option so we can add the conditions.
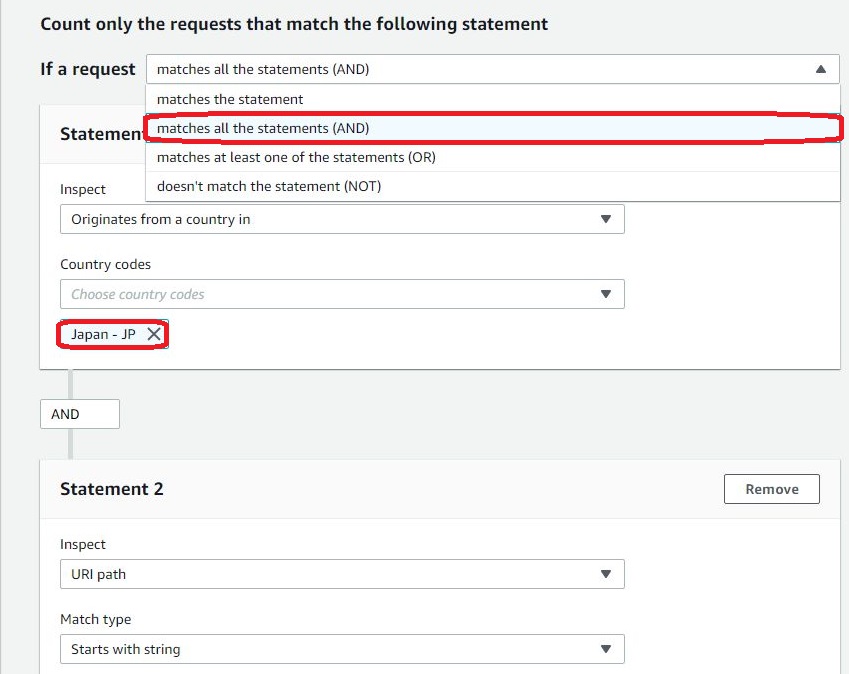
Select AND condition to add limitations based on countries. In the console, we will input options to only allow access from Japan, but we will edit the condition to adjust the setting to add exclusion condition later in the JSON editor.
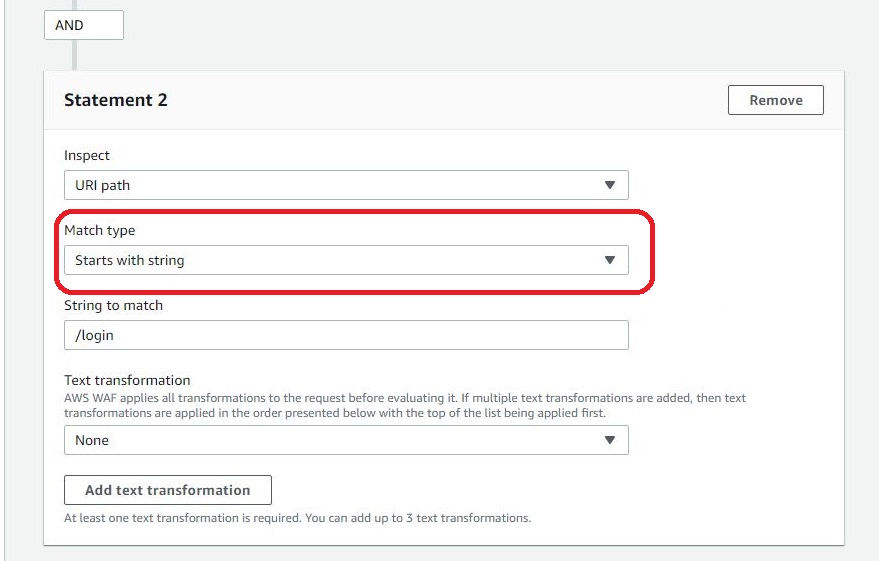
Add another ADD statement to apply the URI condition and set the match type to the “Start with string” option.
The options you can add in visual editors have been all set. In order to adjust the condition to block access from countries other than Japan, we need to switch to the JSON editor.
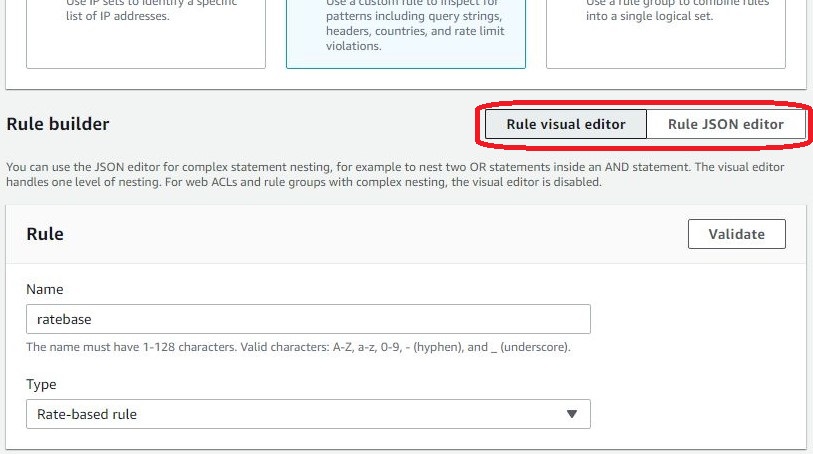
Edit using JSON editor
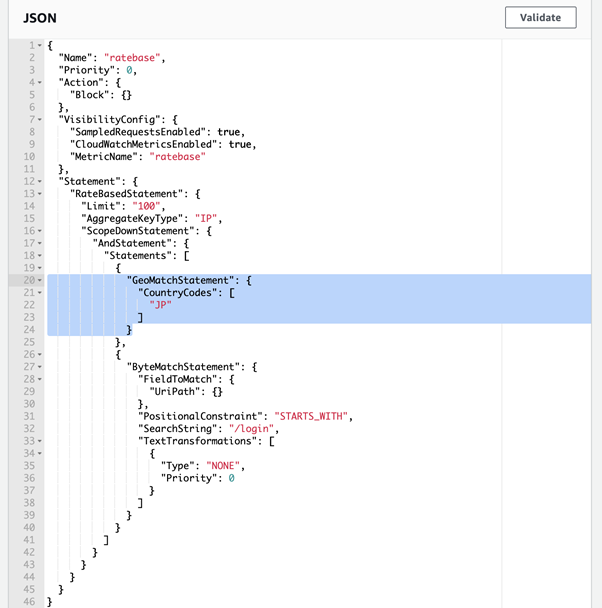
When you open the JSON editor, you will see the options you’ve set in the visual editor before. We will be adjusting the settings under “GeoMatchStatement” shown below.
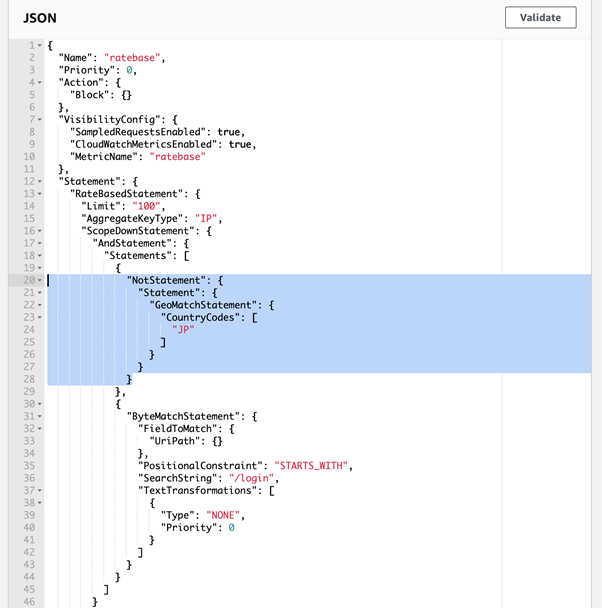
You need to declare to use NotStatement and enclose the GeoMatchStatement within the NotStatement as shown below.
If you are familiar with the process, you can write the whole rule using the JSON editor, but it is easier to use the visual editor when possible.
5. Limitations when using WafCharm
We do accept the customization for rate-based rules. Please contact us to apply a custom rule.
If you want to create your own rule, please avoid using the rule name that starts with "WafCharm."
6. Conclusion
It is a difficult rule to utilize, but you could also set the action of the rate-based rule to COUNT and add the matched IP addresses to the blacklist. If having numerous requests is abnormal for your website, it might be helpful to consider adding the rule.




